I get asked a lot about whether taxing soda is effective. There has been a lot published on taxing food and beverages that are deemed bad for us. So what gives? Does taxing soda have any impact on our health? This is my take on the science, but first, let this jig run through your head….
Should five percent appear too small
Be thankful I don't take it all
'Cause I'm the taxman
Yeah, I'm the taxman
I'll tax the street
(If you try to sit, sit) I'll tax your seat
(If you get too cold, cold) I'll tax the heat
(If you take a walk, walk) I'll tax your feet
TAXMAAAAAAAN!!!
Sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) are nonalcoholic beverages containing added caloric sweeteners. In addition to carbonated soft drinks or sodas, SSBs include energy and sports drinks, less-than-100-percent fruit or vegetable juices, ready-to-drink teas and coffees, sweetened waters, and milk-based drinks. SSBs are widely consumed worldwide, and the retail sales of these beverages have been increasing over the last decade. Their consumption has been associated with obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and other detrimental non-communicable diseases (NCDs). Because of their unhealthy nature, the World Health Organization has included a range of policy priorities, including SSB taxes, to help countries combat NCDs and improve the overall health of the global population.
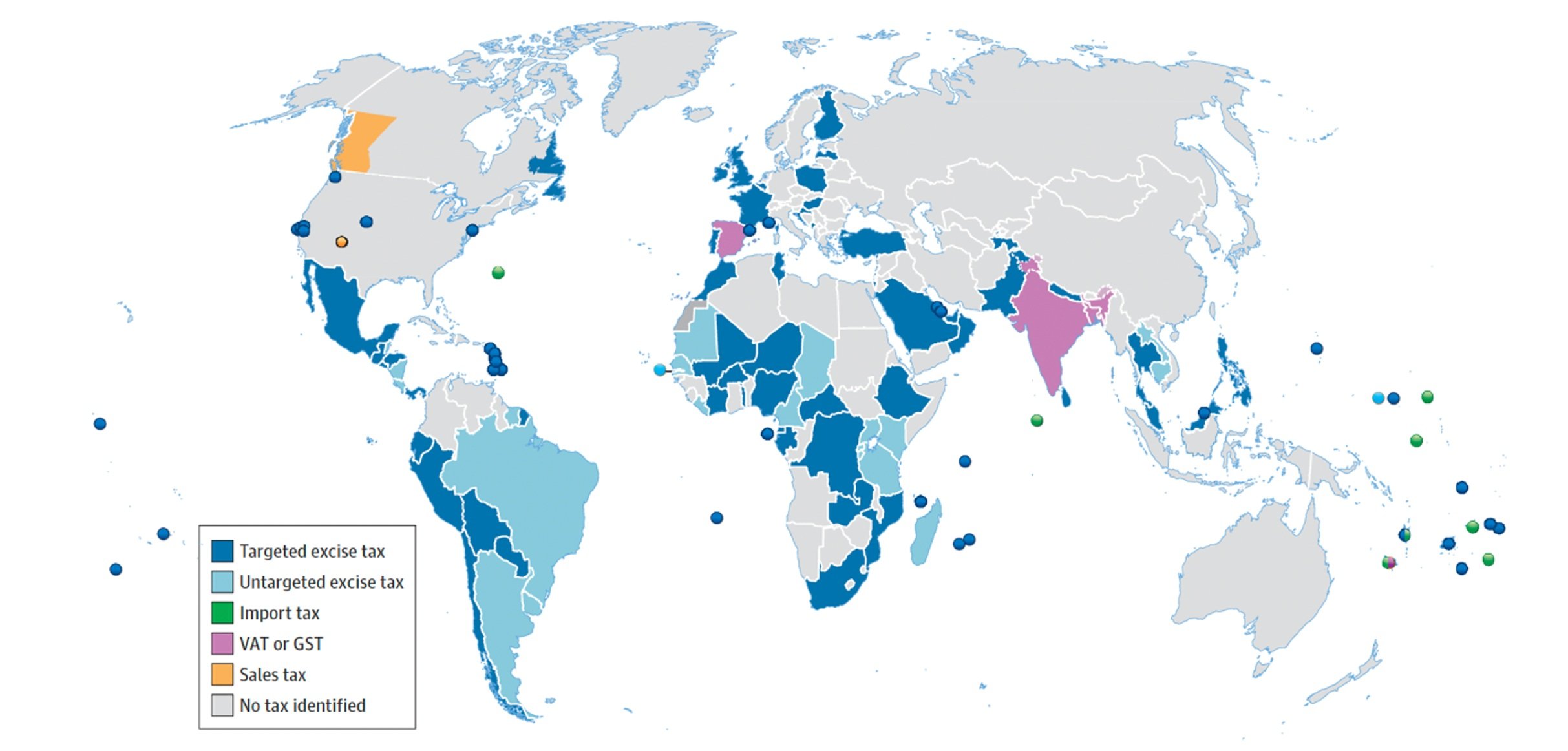
Taxes on SSBs have been introduced in 118 countries, with 105 at the national level and 13 at the subnational level, covering 51% of the world’s population. Most SSB taxes are implemented using excise taxes (88%), with a handful of other countries implementing them through mechanisms such as import taxes, differential Value-Added Tax (VAT), Goods and Services Tax (GST), or regional sales tax (see the figure below). These excise taxes occur mainly as tax pass-throughs, in which the price increase of the taxed product falls on the consumer. In the U.S., for example, 70% of SSB taxes are passed onto consumers through higher-priced SSBs.
In a systematic review and meta-analysis of 62 empirical studies of SSB taxes across 45 countries, the majority of SSB taxes were implemented as a tax pass-through. While the impacts were heterogeneous across the countries, the demand for SSBs was sensitive to tax-induced price increases, with a mean reduction in sales of SSBs by 15%. The sales resulted in no substitution towards healthier, untaxed beverages (e.g., bottled water). Another review argued that SSB taxes provide no substantive changes to dietary or purchasing behavior due to the lack of substitution towards healthier alternatives. Another study found that while SSB taxes modestly reduced the purchases of some taxed beverages in the taxing jurisdiction, consumers respond to the taxes by increasing cross-border shopping, in which they go outside the taxing jurisdiction and buy those same taxed beverages at a lower cost. However, taxes may spur downstream effects on other industry responses and policies, including reformulating products to reduce sugar consumption in those beverages, as was seen with the graduated sugar tax implemented in the UK.
Of the tax policies around the world, 73% are implemented in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), with the highest in South Asia. However, LMICs face many challenges in implementing SSB taxes, including a lack of political will and resources, weak national capacity to implement policies, large informal food sectors, and substantial influence of the food and drink industry on policy development.
The question remains whether SSB taxes can result in healthier dietary patterns and reduce the health implications accompanying excess consumption of these products – particularly NCDs. Most of the evidence — particularly from Nakhimovsky et al., 2016; Niebylski et al., 2015; Teng et al., 2019; and Thow et al., 2014 — suggests that SSB taxes have impacted the purchases of taxed products to varying degrees, but not necessarily long-term and impactful behavior change towards healthier diets and improvements in health. One potential reason may be that the SSB taxes translate to only a 5 to 22-kilocalorie reduction per capita daily. This is insufficient to have a meaningful impact on disease outcomes. Some researchers suggest that one way to deal with this is to raise the current tax rates from the current approximate 5% to 20%. This would also be aligned with the WHO’s recommendation for at least a 20% tax on SSBs. Several countries, such as Qatar and Saudi Arabia, have substantive (50-100%) excise taxes on SSBs, which are more in line with the taxation rates of tobacco.
The question is whether other foods, particularly red meat, should be taxed due to their significant implications on the environment and contributions to climate change. While consuming red meat in high amounts can contribute to NCDs, red meat is also a source of important nutrients. If a tax on red meat makes them prohibitively expensive for those who already struggle to afford these foods, it could put these nutrient-dense foods even further out of reach for the world’s poor. Thus, a “carbon tax” on red meat might be appropriate in wealthy countries with strong social protective measures and in countries with disproportionately high levels of red meat consumption.